National Estuarine Eutrophication Assessment Website & Survey
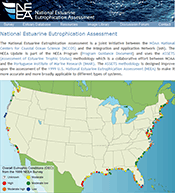 The National Estuarine Eutrophication Assessment (NEEA) is a joint initiative between the NOAA National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science (NCCOS) and the Integration and Application Network (IAN). IAN has just launched the new NEEA website, which consists of a database of 141 U.S. estuaries with satellite imagery, maps (including salinity zone information), location, physical characteristics, landuse & population, hydrology, climate, oceanic details, sediment & nutrient loads, an image library, and discussion forum. The NEEA website also contains an interactive survey designed to gather information on these estuaries in preparation for an update to the original assessment released in 1999. The survey provides immediate feedback to the user by calculating eutrophication symptom expressions for a variety of parameters as well as an assessment of the overall eutrophic condition of the estuary based on their entered data. The site also features dynamic graphing of the database and survey data.
The National Estuarine Eutrophication Assessment (NEEA) is a joint initiative between the NOAA National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science (NCCOS) and the Integration and Application Network (IAN). IAN has just launched the new NEEA website, which consists of a database of 141 U.S. estuaries with satellite imagery, maps (including salinity zone information), location, physical characteristics, landuse & population, hydrology, climate, oceanic details, sediment & nutrient loads, an image library, and discussion forum. The NEEA website also contains an interactive survey designed to gather information on these estuaries in preparation for an update to the original assessment released in 1999. The survey provides immediate feedback to the user by calculating eutrophication symptom expressions for a variety of parameters as well as an assessment of the overall eutrophic condition of the estuary based on their entered data. The site also features dynamic graphing of the database and survey data.
Bay Grass Restoration in Chesapeake Bay
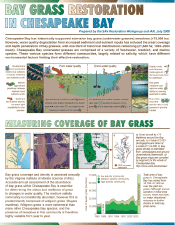 A new science newsletter synthesizing underwater bay grass restoration techniques, success, and recommendations in the Chesapeake Bay is now available. This newsletter is the product of two workshops organized by the Integration and Application Network for the 'SAV Restoration Workgroup', with funding by Maryland Department of Natural Resources. The workshops were held in April 2004 and March 2005, with participants from UMCES, Maryland Department of Natural Resources (MD DNR), Virginia Institute of Marine Science, US Geological Survey, and National Oceanographic & Atmospheric Administration Chesapeake Bay Office. The workshops discussed the status of MD DNR’s restoration targeting model, and determined the different bay grass habitats within the Bay. As part of this effort, the IAN website also hosts a webpage to facilitate discussion of the community diagrams produced as part of the workshop. The findings presented in the newsletter can also be discussed on the IAN forum. IAN newsletters are available as PDFs from our website, or you can order printed copies for your organization on the IAN newsletters page.
A new science newsletter synthesizing underwater bay grass restoration techniques, success, and recommendations in the Chesapeake Bay is now available. This newsletter is the product of two workshops organized by the Integration and Application Network for the 'SAV Restoration Workgroup', with funding by Maryland Department of Natural Resources. The workshops were held in April 2004 and March 2005, with participants from UMCES, Maryland Department of Natural Resources (MD DNR), Virginia Institute of Marine Science, US Geological Survey, and National Oceanographic & Atmospheric Administration Chesapeake Bay Office. The workshops discussed the status of MD DNR’s restoration targeting model, and determined the different bay grass habitats within the Bay. As part of this effort, the IAN website also hosts a webpage to facilitate discussion of the community diagrams produced as part of the workshop. The findings presented in the newsletter can also be discussed on the IAN forum. IAN newsletters are available as PDFs from our website, or you can order printed copies for your organization on the IAN newsletters page.
'Bar Cleaning' in Oyster Restoration
 A Consensus Statement from the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science. July 11, 2005 'Bar cleaning,' or the removal of as many existing oysters as feasible on a bar prior to planting disease-free seed oysters, has become a regular component of oyster restoration projects in Maryland. Recently a proposal has been put forward to expand the scope of bar cleaning. Scientists with expertise in oyster biology, restoration, and management within the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science (UMCES) met to discuss their diverse perspectives on bar cleaning and power dredging. They developed the consensus statement to offer the Center’s best scientific advice to decision makers, managers, stakeholders, and partners in oyster restoration.
A Consensus Statement from the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science. July 11, 2005 'Bar cleaning,' or the removal of as many existing oysters as feasible on a bar prior to planting disease-free seed oysters, has become a regular component of oyster restoration projects in Maryland. Recently a proposal has been put forward to expand the scope of bar cleaning. Scientists with expertise in oyster biology, restoration, and management within the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science (UMCES) met to discuss their diverse perspectives on bar cleaning and power dredging. They developed the consensus statement to offer the Center’s best scientific advice to decision makers, managers, stakeholders, and partners in oyster restoration.
New IAN Personnel
 Earlier this year, UMCES hired Michael Williams to be a Water Quality Analyst at the Chesapeake Bay Program Office in Annapolis, MD. In this position, he provides analytical support to the Tidal and Nontidal Water-Quality Workgroups. His previous research has focused on natural and human-induced disturbances in watersheds, such as landuse change, and their biogeochemical effects on receiving waters. Michael's degrees include a BA in Aquatic Biology from the University of California at Santa Barbara, a MS in Estuarine and Environmental Sciences from the University of Maryland, and a doctorate in Aquatic Chemistry from the University of California at Santa Barbara. His time outside of work is spent with his Brazilian wife, Solange, 9-year old daughter, Isabella, and a Sheltie named Bidu. Please join us in welcoming Michael to the Integration and Application Network of UMCES.
Earlier this year, UMCES hired Michael Williams to be a Water Quality Analyst at the Chesapeake Bay Program Office in Annapolis, MD. In this position, he provides analytical support to the Tidal and Nontidal Water-Quality Workgroups. His previous research has focused on natural and human-induced disturbances in watersheds, such as landuse change, and their biogeochemical effects on receiving waters. Michael's degrees include a BA in Aquatic Biology from the University of California at Santa Barbara, a MS in Estuarine and Environmental Sciences from the University of Maryland, and a doctorate in Aquatic Chemistry from the University of California at Santa Barbara. His time outside of work is spent with his Brazilian wife, Solange, 9-year old daughter, Isabella, and a Sheltie named Bidu. Please join us in welcoming Michael to the Integration and Application Network of UMCES.